Description
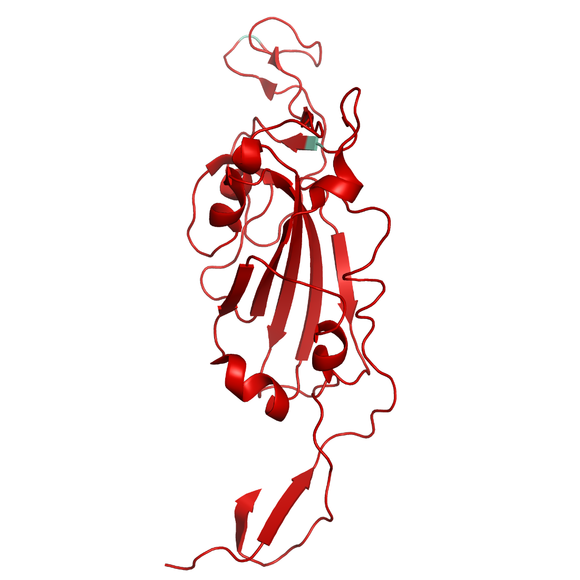
Recombinant protein of the receptor binding domain (RBD), Mutant (L452R-T478K) of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-2019) Spike S1 from Wuhan pneumonia virus with C-terminal His-Tag. The mutations L452R-T478K are characteristic for the fast spreading SARS-CoV-2 virus variants B.1.617 emerged in India. These mutations are affecting the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein, which the virus uses to bind to human cells receptors and enter them. Due to the mutations, the virus is allowed to bind with higher affinity to human ACE2 receptor which results in increased transmissibility of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
-
Product Name: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Spike S1 Protein (RBD, Mutant (L452R, T478K)), His-Tag
- Catalog No.: P2020-060
- RefSeq Links: NC_045512.2; MN908947.3; YP_009724390.1; QHD43416.1; GeneID: 43740568; UniProt: P0DTC2
-
Synonyms: SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD; SARS-CoV-2 spike protein; 2019-nCoV; COVID-2019; COVID-19; RBD (L452R, T478K); 501.V2; VUI-202012/01; B.1.617; B1617; B.1.617.1; B16171; B.1.617.2; B16172; B.1.617.3; B16173; Indian Variant; Delta; E484Q; T478K